Environment Constraints
Prerequisite: understand the environment concept offered by Delivery Configs
What is an Environment Constraint?
Environment constraints control how an artifact version flows through environments. A constraint can
be as simple as ensuring an artifact isn’t promoted into Environment B unless it has successfully deployed into
Environment A. Constraints can also specify that an artifact needs to have a canary evaluated by Kayenta before
it can be deployed into an environment, while also defining how the canary should be deployed and evaluated.
Defining Constraints
Every environment defined in a Delivery Config supports a top-level constraints list property.
The following example ensures that artifact versions are only promoted into the staging environment after
successful deployment to the test environment, and only if the current time is within the days Monday thru
Thursday and the hours of 8am and 4pm.
environments:
- name: staging
resources: # omitted for brevity
notifications: # omitted for brevity
constraints:
- type: depends-on
environment: testing
- type: allowed-times
windows:
- days: Monday-Thursday
hours: 8-16
Constraint Types and Ordering
Constraints are currently bucketed into stateless and stateful types. Stateless constraints can always be fully
evaluated in a single pass and do not interact with users or external systems. The current stateless constraint
types are depends-on and allowed-times.
Stateless constraints are always evaluated first, and must be satisfied before any stateful constraints are evaluated. Stateful constraints are a powerful construct, with the ability to mutate cloud state during their evaluation. Examples include deploying a new artifact version into an environment for the sake of canary analysis, or launching a smoke-test pipeline against a prior environment, gating promotion on its success.
This implicit ordering by type ensures that a pipeline constraint gating promotion to a production environment on smoke-tests run against a prior environment will only invoke the test pipeline after the artifact version under evaluation is deployed to the prior environment.
All stateful constraints can be manually overridden, such as when a canary failure is deemed to be expected for a given change, or a false alarm. When an environment defines multiple constraints, all must pass before a new artifact is promoted into the environment.
Available Constraints
Depends On
The depends-on constraint ensures that an artifact version will not deploy into the environment it is
attached to, unless it has successfully deployed into the dependent environment.
Parameters
environment: The name of the dependent environment. It must be defined within the same delivery config as
the target environment containing the constraint.
Example
constraints:
- type: depends-on
environment: testing
Allowed Times
The allowed-times constraints provides a time based gate on promotion into an environment. It can be used to
ensure promotion to an environment only occurs during business hours, or quiet times.
Parameters
windows: A list of time windows; multiple windows can be specified on a single constraint. The constraint is
satisfied if the current time matches any single window.
tz: Optional The timezone to evaluate the constraint in. This is optional, by default the timezone specified via
the default.time-zone spring configuration property is used, not the JVM or OS timezone. If your organization
operates in a single timezone, this property should likely be set that timezone.
Window Parameters
hours: Supports ranges (i.e. 10-20) and comma separated lists (i.e. 5,6,7,8) or a combination
of the two.
days: Supports aliases (weekdays and weekends), as well as ranges and comma separated lists of
days in their java standard (java.util.Calendar) short (mon-thu) or full (monday-thursday) names.
Example
constraints:
- type: allowed-times
windows:
- days: Monday-Wednesday,Friday
hours: 8-16
- days: Thursday
hours: 14-16
This allows artifacts to deploy into the environment between 8am-4pm on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, and Friday or between 2-4pm on Thursday.
Manual Judgement
The manual-judgement constraint prevents an artifact from deploying to an environment without explicit
approval via an external API client. UI support for approving or rejecting judgements as well as an
interactive slack bot are under development but direct use of Spinnaker’s REST API is currently required to
answer a manual judgement. See
Interacting with and Overriding Constraints
for details.
Parameters
timeout: (Optional); Type: Duration; Default Value: PT1W
If judgement is not provided within this time (starting when the constraint is initially evaluated for a given environment and artifact version), it is considered rejected.
Example
constraints:
- type: manual-judgement
Pipeline
The pipeline constraint launches a pipeline, optionally passing along constraint provided trigger
parameters. The pipeline execution is periodically monitored and the constraint status derived from
the final status of the execution.
Parameters
pipelineId: Type: String
The configuration id of the pipeline to be executed during constraint evaluation. If unknown,
edit the given pipeline from the Spinnaker UI. From the edit configuration view, the pipelineId is the
final part of the URL. The pipeline can be a part of any application, but must be runnable via
the service account defined in the target environment’s delivery config.
retries: (Optional); Type: Integer
If set, pipeline failures will be retried up-to this many times if pipeline execution goes terminal for any reason. The constraint evaluation will fail once retries are exhausted.
parameters: (Optional); Type: Map<String, Object>
If set, the contents of this map are passed as trigger parameters when executing the pipeline. Expressions are not currently supported.
timeout: (Optional); Type: Duration; Default Value: PT2H
If the pipeline execution does not complete within this time, it is considered a failure.
Example
constraints:
- type: pipeline
pipelineId: fn0rd5d1-6217-4fcf-aa3d-ce7f59af9cac
retries: 1
parameters:
foo: bar
Canary
The canary constraint supports deploying experiment and control clusters across multiple regions within
the target environment. Experiment/control cluster health is evaluated via Kayenta and the clusters
removed once evaluation is complete. By default, a multi-region constraint must pass in all regions
for the constraint to pass but this behavior is configurable.
The canary constraint currently only supports EC2. Keel configuration properties may need to be set
depending on how Kayenta accesses time-series data and persists state.
System Configuration Properties
defaults.constraint.canary.metrics-account: Default Value: atlas-global.prod
Unless your time series data is stored in Netflix Atlas, this should be set to the equivalent value used with the Orca Kayenta stage.
defaults.constraint.canary.storage-account: Default Value: s3-objects
This should be set to the value of Kayenta’s default-storage-account.
Parameters
canaryConfigId: Type: String
The configuration id of the canary rules used for evaluation. If unknown, select a specific
configuration from Spinnaker’s Canary Config UI. The canaryConfigId is the final segment of the resulting url.
beginAnalysisAfter: (Optional); Type: Duration; Default Value: PT10M
After the deployment of canary clusters completes, Spinnaker will wait this amount of time before launching the first Kayenta analysis. This allows for the filtering or inclusion of service warmup behavior in the analysis.
canaryAnalysisInterval: (Optional); Type: Duration; Default Value: PT30M
After the completion of any beginAnalysisAfter delay, Kayenta analysis are launched at this recurring interval,
until post-beginAnalysisAfter runtime exceeds the lifetime parameter.
lifetime: (Optional); Type: Duration; Default Value: PT30M
Maximum runtime for the canary, exempting deployment times and any initial delay configured via beginAnalysisAfter.
cleanupDelay: (Optional); Type: Duration; Default Value: 0
When a canary fails due to a failing Kayenta score, Spinnaker will wait this amount of time before deleting canary clusters. Useful if engineers desire an opportunity to manually inspect instances involved in the failure.
marginalScore: Type: Integer
If Kayenta generates a canary score below the marginalScore, it is considered an immediate failure.
passScore: Type: Integer
If Kayenta generates a final canary score >= passScore, the constraint will pass.
regions: Type: Set<String>
Each region will get its own independently deployed and analyzed control/experiment pair.
capacity: Type: Integer
Control and experiment clusters have their min/max/desired pinned to this value.
source: Type: CanarySource
Defined in yaml as a Map<String, String> with the following properties:
accountcloudProvidercluster
This should refer to an active cluster in the target environment deployed in all of the regions the constraint is configured to run canaries in. Control/experiment clusters are configured based on the source cluster (i.e. account, subnet, instance type, firewall rules).
minSuccessfulRegions: (Optional); Type: Integer; Default Value: 0
If set to >0 on a multi-region canary, the constraint will pass if Kayenta analysis passes in this many regions. I.e. if set to 2 on a constraint that defines a 3-region canary, the failure of a single region is ignored.
failureCancelsRunningRegions: (Optional); Type: Boolean; Default Value: true
If true, the failure of any region
that violates the minSuccessfulRegions parameter triggers the immediate cancellation of any canaries still
running in other regions.
metricsAccount: (Optional); Type: String
If set, overrides the defaults.constraint.canary.metrics-account property.
This may be required in environments with multiple TSD instances.
storageAccount: (Optional); Type: String
If set, overrides the defaults.constraint.canary.storage-account property. Not typically required.
Example
constraints:
- type: canary
canaryConfigId: fn0rd5d1-6217-4fcf-aa3d-ce7f59af9cac
beginAnalysisAfter: PT3M
canaryAnalysisInterval: PT10M
lifetime: PT90M
marginalScore: 75
passScore: 90
capacity: 2
source:
account: appaccount
cloudProvider: aws
cluster: app-prod
regions:
- us-east-1
- us-west-2
- eu-west-1
minSuccessfulRegions: 2
Interacting with and Overriding Constraints
Apart from the depends-on constraint, all constraint types either expect interaction from a user (in the case of manual-judgement ) or can have their automated judgements overruled by a user.
Approving or rejecting Manual Judgement constraints from Slack
If your operator has configured Slack app integration with Spinnaker, then a very convenient way to approve managed deployments gated by a Manual Judgement constraint is to use interactive Slack notifications.
All you need to do is set up Slack notifications in your delivery config, which will enable interactive notifications to a Slack channel of your choice, where you can simply click a button to approve or reject the deployment of the artifact into the environment.
Consider the following simplified delivery config:
name: myspinapp
application: myspinapp
serviceAccount: myteam@mycompany.com
artifacts:
- name: myspinapp
type: deb
environments:
- name: test
constraints:
- type: manual-judgement
notifications:
- type: slack
address: "#myteam"
frequency: verbose
resources:
- apiVersion: bakery.spinnaker.netflix.com/v1
kind: image
spec:
artifactName: myspinapp
baseLabel: RELEASE
baseOs: xenial
regions:
- us-east-1
storeType: EBS
application: myspinapp
- apiVersion: "ec2.spinnaker.netflix.com/v1"
kind: "cluster"
spec:
moniker:
app: "myspinapp"
imageProvider:
deliveryArtifact:
name: "myspinapp"
type: "deb"
locations:
account: "test"
regions:
- name: "us-east-1"
Upon evaluating whether a new Debian artifact for myspinapp should be deployed into the test environment,
Spinnaker will gate the deployment on the manual-judgement constraint and send a notification that looks like
the following to the #myteam Slack channel.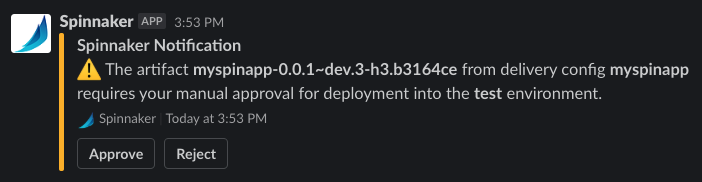
Once a user in the channel clicks on the Approve button, the notification changes to reflect the approval: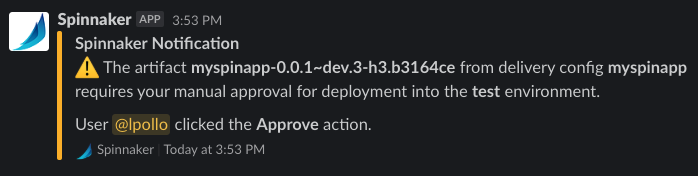
:warning: Note that the
frequencysetting for notifications does not affect this behavior – interactive notifications will always be sent unless your operator has chosen to disable this feature entirely on your company’s instance of Spinnaker.
APIs to interact with constraints
In addition to Slack integration, the following API endpoints are currently available to interact with constraints.
Note: we limit to one delivery config per app, so these APIs currently use app name.
Reading status of pending and recent constraints
GEThttps://gate/managed/application/{application}/environment/{environment-name}/constraints?limit=20
Returns: List<ConstraintState> consisting of:
String deliveryConfigName;
String environmentName;
String artifactVersion;
String type;
String status;
Instant createdAt;
String judgedBy;
Instant judgedAt;
String comment;
Map<String, Object> attributes;
Setting or Overriding Constraint State
POSThttps://gate/managed/application/{application}/environment/{environment-name}/constraint
POST Body:
{
"type": "canary",
"artifactVersion": "fnord-1.2.3",
"status": "OVERRIDE_PASS",
"comment": "overriding false positive kayenta failure"
}
Valid status values: PENDING, PASS, FAIL, OVERRIDE_PASS, OVERRIDE_FAIL